Resistance to antibiotics: a problem of all
The resistance to antibiotics It is a serious health problem that is aggravating year after year, despite the information and awareness campaigns that have been carried out by the health authorities and various social organizations.
According to the first data of the epidemiological study just presented by the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiologyevery year more than 35,000 people die from infections caused by multiresistant bacteria. This means that superbugs kill 30 times more than road accidents, which were 1,200 in 2017 according to the Traffic Department.
Currently, Spain is the first country in the world in antibiotic consumption and it is expected that by 2050 the number of deaths due to antimicrobial resistance will surpass those caused by cancer.
The study was conducted in 82 Spanish hospitals with data from 903 patients with this type of infection. Specifically, one in five patients infected by multiresistant bacteria, 196%, died during the first month of diagnosis of the infection. Extrapolating this data to the rest of the country's hospitals,It is estimated that of the 180,600 patients with infections due to multiresistant bacteria, 35,400 died.
Antibiotic resistance: a global problem
Outside our borders, it is estimated that 700,000 people in the world die every year due to resistance to antibiotics and if the trend does not change, we will talk about ten million victims per year by 2050, always with WHO as a source. So we are talking about an epidemic that will kill more people than cancer, if we do not remedy it.
Resistance to antibiotics is, therefore, a social problem and, even, referring to our country, cultural. The widespread and ingrained habit of self-medicating without the health professional and treating the child with antibiotics "as soon as he has mucus", as well as the social pressure exerted on the doctors, make this problem perpetuate, without seeing a short-term solution. The false image that the patient is better protected with antibiotics is difficult to change in the popular imagination.
We can not neglect the use and abuse of antibiotic treatments of livestock and animals for human consumption, whose meat is part of the food chain. Said antibiotics contribute in an important way in creating resistance to the consumers of said treated meat. They are, therefore, these two causes the great generators of resistance: the misuse in humans and abuse in animals. We are facing a serious problem in which the population has not repaired or given importance until recently.
What effects does inadequate antibiotic use produce?
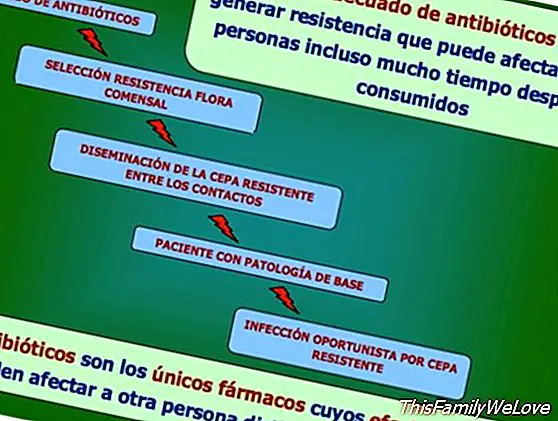
Treat a viral process, usually respiratory at this time of year, with an antibiotic is useless and subject the patient to unnecessary risks (allergic reactions, diarrhea and other adverse effects). In addition, the ecological impact on the respiratory and intestinal flora is considerable, since the antibiotic will eliminate the majority population of sensitive bacteria and will favor the growth of the resistant bacterial population and its possible subsequent dissemination.
The extent of antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is increasing worldwide to dangerous levels. Day after day, new mechanisms of resistance are appearing and spreading all over the planet that endanger our ability to treat common infectious diseases. A growing number of infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, septicemia, gonorrhea or foodborne diseases are increasingly difficult - and sometimes impossible - to treat as antibiotics lose effectiveness.
Ideas to prevent antibiotic resistance
The general population, all of us, can take a series of preventive measures to avoid resistance to antibiotics:
1. Do not self-medicate and take antibiotics only when prescribed by a certified healthcare professional.
2. Always follow the doctor's instructions regarding the dose and time of treatment, and not leaving prematurely when the patient is better.
3. Do not ask for antibiotics much less to pressure the doctor, if the professional does not consider it appropriate to prescribe them. A stressed and tired doctor can give in to the insistence of parents alarmed by their child's fever and little informed about the consequences of the misuse of drugs.
4. Prevent infections washing hands and preparing food in hygienic conditions, especially when there are patients at home, and adopting protective measures in sexual relations.
5. Get vaccinated following the official vaccination calendar that the health authorities advise.
Obviously, the solution to curb resistance to antibiotics also goes through other types of measures that the administration must implement:
- prescription of antibiotics with a prescription
- invest in research and development of new antibiotics
- information and dissemination campaigns on how to avoid infections and the harmful effects of the inappropriate use of certain drugs, and specifically, of antibiotics
- greater control over the use of antibiotics and other drugs in livestock and animals intended for human consumption.
In short, although these measures are beyond the reach of the population in general, we can collaborate not to worsen the situation through adequate information and rational use of antibiotics, relying on the prescription of health professionals and taking into account Count the waves precautions previously indicated.
This is how bacteria get resistant to antibiotics
For those who want to know more about this topic, it will be interesting to know that bacteria have some biological characteristics that facilitate the acquisition of resistance to antibiotics:
to. Bacteria have a high duplication rate, being able to double its population in thirty minutes in suitable culture media, presenting a high rate of spontaneous mutations, which favor the appearance of resistance: if due to chance one of these mutations allows them to survive in the presence of an antibiotic, the same selective pressure This one (kills all sensitive bacteria) will favor the emergence of a resistant population.
b. Resistances that result from the acquisition of genetic material foreign to the bacterium and that gives it some capacity that allows it to survive the antibiotic, as is the case of plasmids. These are extrachromosomal DNA molecules that replicate and transmit independent of chromosomal DNA. The number can vary from a single copy up to a few hundred per cell. In general, they do not confer essential information, but they confer advantages to the host. The most common example is that of plasmids that contain genes for resistance to a particular antibiotic.
Once the resistance is acquired, it can be disseminated in two ways:
- by dispersing the same resistant strain
- through the dispersion of genes that generate it through mobile genetic elements such as plasmids.
In addition, resistant bacteria can be quartered in certain reservoirs from which they can begin their dissemination to the rest of the population. These reservoirs can be farm animals, certain patients multitratados with antibiotics, certain centers such as ICU (intensive care units), or chronic patients.
Dr. Román Rodriguez Barriguete. General Physician and Physician of the Work of FCC




